- Fruit
- Edible Oil
- Stuffed Pasta
- Crops Grains Oilseeds and Rice
- Grain Milling and Malt
- Vegetable Dried Beans
- Natural Plant Spices
- Nuts and Seeds
- Dried Fruits
- Unroasted coffee&cocoa beans
- Special Dietary Foods
- Functional foods
- Eggs and egg products
- Meat and meat products
- Aquatic products
- Aquatic Animals
- Dairy
- Casings
- Bird's Nest
- Bee products
- GMO
- Non-edible animal products
- Chinese herbal medicine
- General Foods
- GACC Evaluates CA
- Cotton Supplier Registration
Chinese herbal medicine
Chinese medicinal materials refer to the medicinal parts of medicinal plants and animals, and the raw medicinal materials formed after primary processing after harvesting.
GACC registration conditions for overseas manufacturers of imported foods are as follows:
1. The food safety management system of the country/region where the manufacturer is located has passed GACC's equivalence assessment and/or review;
2. The manufacturer was established with approval by the competent authority of the country/region, and the manufacturer is under effective regulation by the competent authority;
3. The manufacturer has an established, effective food safety and sanitation management system and protection system, legally produces and exports food in the country/region, and ensures that foods exported to China comply with relevant Chinese laws, regulations, and national food safety standards;
4. Food exporting to China conforms with relevant inspection and quarantine requirements that have been agreed upon after discussion by the GACC and the competent authorities of the country/region.
The quarantine access of imported herbal medicines and the registration of overseas production enterprises have been adjusted to the new department and group of experts of the General Administration of Customs, and no longer refer to the "Catalogue of Food Products Imported to China from Countries or Regions Meeting the Requirements for Assessment and Review and Has Traditional Trade with China" The herbal medicine module of the catalog has recently been taken offline, and the new data must be referred to determine the quarantine access status, the enterprise registration conditions, procedures and required materials for specific herbal medicines. It should be emphasized that this is a brand new change and the fragmented information on the internet is almost all stuck in the old mode. It is recommended to communicate with us for confirmation before implementation to get straightforward and correct guidelines so as not to be misled by the complicated information.
Access steps for overseas Chinese herbal medicine manufacturers:
-
01
Overseas manufacturers should fully understand the requirements of the laws and regulations of the exporting country or region, the mandatory requirements of China's national technical specifications, and the inspection and quarantine requirements.
-
02
Submit an application to the local competent authority of the exporting country or region;
-
03
The relevant laws and regulations on animal and plant epidemics, veterinary health, public health, plant protection, enterprise registration management, etc. in the country or region where you are located, and the written information on the establishment and personnel of the competent authority in the country or region, and the implementation of laws and regulations, etc.
-
04
List of overseas production enterprises applying for registration;
-
05
The assessment conclusion conducted by the competent authority of the country or region where the companies are recommended of the actual situation of epidemic prevention and hygiene control;
-
06
A statement by the competent authority of the country or region where the overseas producers it recommends meets the requirements of Chinese laws and regulations;
-
07
Enterprise registration application, floor plan, process flow chart, animal or phytosanitary prevention and control system documents of plant, workshop and warehouse, photos of epidemic prevention and disinfection treatment facilities, photos of waste and packaging harmless treatment facilities, etc.
-
08
After the General Administration of Chinese Customs(GACC) has received the recommended materials and passed the written examination, after consultation with the competent authority of the exporting country or region, GACC may send personnel to the exporting country or region to evaluate its supervision system, and carry out the evaluation of the overseas production enterprises. After inspection, the applicant enterprises that meet the requirements shall be registered.
-
09
The General Administration of Chinese Customs(GACC) releases the list and updates the catalog at the same time.
Our assistance:
1. Assist in sorting out the requirements of the laws and regulations of the exporting country or region, the mandatory requirements of China's national technical specifications, and the inspection and quarantine requirements.
2. Assist the overseas enterprise to review the registration elements, complete the self-assessment, and provide continuous improvement plans according to the assessment results, so as to meet the registration conditions and the mandatory requirements of the Chinese technical specifications. Assist in sorting, screening, editing, and translating the required materials, so that the application materials meet the integrity, authenticity and validity requirements.
3. Assist in completing all application materials, fill in the application form and submit the application to the competent authority.
4. Follow up the application flow of competent authorities, embassies and GACC.
5. Materials correction, when the written materials do not meet the registration requirements, assist the enterprise to complete the interpretation, sorting, screening, editing, translation, calibration and other standards and laws and regulations of the required materials within the specified time.
6. Acceptance by Chinese Customs and follow-up and communication of technical review by expert group, preparation and coordination before on-site review or video review.
7. Assist in successful access and follow up on the use of registration data for customs clearance, and respond immediately if there are any problems.
8. Other enterprise access and follow-up related support.
1. Quarantine access
As required, animal derived traditional Chinese medicinal materials require overseas enterprise to register, however, the import of plant-based Chinese medicinal materials generally does not require the overseas enterprises to register (if the plant-based Chinese medicinal materials have traditional trade records before, the registration of overseas enterprises is not required. For newly applied varieties, registration shall be made by the overseas enterprises if it's needed according to the requirements of both parties' protocols.) For details, please check the List of Approved Imported Chinese Medicinal Materials and Exporting Countries and Regions in the customs website. From November 2022, the work including the quarantine access and registration of overseas enterprises for animal and plant derived Chinese medicinal materials with high quarantine risks shall be responsible by the new department of the General Administration of Customs. The “List of Countries and Regions That Export Food to China and Meet the Evaluation and Review Requirements and Have Traditional Tradition” shall not be referred. The Chinese medicinal materials module in this catalog has recently been offline, and new data must be used to determine the specific quarantine access status, enterprise registration conditions, procedures, and required information of the Chinese medicinal materials. It should be emphasized that this is a completely new change, and almost all fragmented information on the internet remains in the old mode. It is recommended to communicate and confirm with us before implementation to obtain direct and correct guidance to avoid being misled by complex information.
The risk assessment and review on the equivalence of the regulatory system for traditional Chinese medicinal materials in the country (region) of origin conducted by General Administration of Customs:
(1) Sort out the relevant laws and regulations on animal and plant epidemics, veterinary hygiene, public health, plant protection, enterprise registration management, etc. in the country or region of origin, as well as written materials on the establishment and personnel situation of the competent department in the country or region of origin, as well as the implementation of laws and regulations;
(2) Application. The intended exporting country (region) shall submit an application to the General Administration of Customs for export to China in written. The General Administration of Customs initiates the admission process and provides a risk assessment questionnaire to the intended exporting country;
(3) Organize evaluation. The intended exporting country will reply based on the questionnaire, provide relevant technical information, and the General Administration of Customs will conduct a risk assessment. As required, an expert team will be dispatched to visit overseas for investigation;
(4) The General Administration of Customs shall negotiate with the competent authorities of the exporting country or region to determine the quarantine requirements for exporting Chinese medicinal materials to China based on risk analysis and evaluation review results, sign relevant protocols, and determine quarantine certificates;
(5) Enterprises shall register in the General Administration of Customs according to the specific requirements of the protocol, and the General Administration of Customs shall publish a list of products of the countries or regions that meet the evaluation and review requirements;
2. Registration of overseas enterprises
According to the results of risk analysis, the General Administration of Customs shall determine the varieties list of medicinal materials that need overseas registration and implement dynamic adjustment. The General Administration of Customs shall implement registration for overseas manufacturers that export medicinal materials to China and need overseas registration. If the access status of the plant derived Chinese medicinal materials is “normal”, the enterprises of this country do not need access registration; if the access status is “allowed to import from registered enterprises”, access registration is required (such as saffron of Greece and Afghan, tuckahoe and blood creeper from Laos, Licorice from Uzbekistan, which have obtained access in the past two years). If the country is not indicated, the General Administration of Customs shall carry out product risk analysis and evaluation of the supervision system on the countries or regions exporting Chinese medicinal materials to China for the first time. After the negotiation on the inspection and quarantine requirements of both parties, a protocol shall be signed. The registration of overseas production enterprises will be implemented according to the specific requirements of the protocol.
3. Quarantine approval
For the imported Chinese medicinal materials need to conduct quarantine approval for imported animals and plants, the owners or their agent should apply for the Quarantine Permit for Imported Animals and Plants through “Internet plus + Customs” in accordance with the provisions of Administrative Measures for the Quarantine Approval of Imported Animals and Plants before signing the trade contract. Animal derived Chinese medicinal materials need quarantine approval, According to Announcement No. 77 of 2024 of the General Administration of Customs (Announcement on Cancelling the Entry Quarantine Approval of Some Animal and Plant Products), the plant-derived Chinese medicinal materials in the following table do not need to apply for an entry animal and plant quarantine license:
| HS Codes | Product Name | CIQ Codes |
| 1211903999 | Other fresh, cold, frozen or dried plants (including certain parts of them, whether cut, crushed or ground into powder) mainly used as medicinal materials (Medicinal Smilax) | 1211903999142 |
| 1211903999 | Other fresh, cold, frozen or dried plants (including certain parts of them, whether cut, crushed or ground into powder) mainly used as medicines (SPATHOLOBCAULIS) | 1211903999315 |
4. Customs clearance form for imported medicinal materials or Permission of imported medicinal materials
The medicinal materials imported for the first time shall be registered in the drug regulatory department at the port after obtaining the permission for import of medicinal materials in accordance with the provisions; The medicinal materials imported for the first time refer to the imported medicinal materials of different countries (regions), different applicants and different origins. For the Chinese medicinal materials in the List of non-First Imported Medicinal Materials, online registration from the port drug supervision and administration department can be made directly obtain Customs clearance form for imported medicinal materials without the permission of imported medicinal materials. If the Chinese medicinal material is listed as an endangered species (Appendix to the Convention on International Trade in Endangered Species of Wild Fauna and Flora), it also needs the National Forestry and Grassland Administration to issue an “administrative licensing decision allowing the import of wildlife products”. For the first time of importing medicinal materials, the applicant shall fill in the application form for import of medicinal materials through the information system of the State Drug Administration, and submit the following information to the local provincial drug regulatory department:
(1) Application form for import of medicinal materials;
(2) Copies of drug production license or license for pharmaceutical trading of the applicant, and if the applicant is the holder of the marketing authorization for Chinese patent medicines, copies of relevant drug approval documents shall be provided;
(3) Copies of the exporter’s principal registration certificate;
(4) Copies of the purchase contract and its notarial documents;
(5) Ecological environment, resource reserves, wild or cultivated situation, information on harvesting and primary processing of origin in the place of origin of medicinal materials;
(6) Standards and standard sources of medicinal materials;
(7) The original copy of the medicinal materials identification of origin, recording identification conclusion, sample picture, authenticator, authenticate organization and its seal, issued by the institution with the qualification of plant base identification in China.
5. Importer qualification
The importer of medicinal materials shall be the holder of the marketing approval for Chinese patent medicines, traditional Chinese medicine manufacturer, as well as pharmaceutical trading enterprises with the business of Chinese medicinal materials or Chinese herbal slices in China. The consignee shall fill in the relevant information through the standard “Enterprise Qualification” subsystem of “China International Trade Singlewindow” or “Enterprise management” subsystem of “Internet + Customs” of General Administration of Customs, and submit the application materials to the customs where industrial and commercial registration locates.
6. Regulations for processing and storage enterprises (only applicable to animal derived Chinese medicinal materials)
Imported animal derived Chinese medicinal materials must be processed and manufactured by designated qualified processing enterprises, and can only go on sale after the qualification assessment procedure completed. For details, please refer to the List of Designated Enterprises for the Storage and Processing of Imported Animal Derived Traditional Chinese Medicine on the customs website. Processing enterprises log on to the “Internet plus + Customs” integrated online service platform( http://online.customs.gov.cn )and enter the “Recordation for the Designated Storage and Processing Enterprise of Imported Traditional Chinese Medicine” section under the column “Enterprise Management and Inspection” to fill in and submit the online application and scanned copies of the above-mentioned paper materials. After accepting the application, competent customs will review the paper recordation application materials submitted by the enterprise, organize a review team to review, and issue a review report. The competent customs shall record, number, and publish enterprises that are qualified after the evaluation.
7. Designated import customs clearance port
Heilongjiang Province: Heihe, Dongning, Suifenhe, Tongjiang
Jilin Province: Ji’an, Changbai, Tumen, Sanhe, Hunchun
Inner Mongolia: Erenhot, Manzhouli
Guangxi: Pingxiang, Dongxing, Longbang, Aidian
Yunnan Province: Ruili, Tianbao, Jinghong, Hekou, mengkang, mohan(including railway ports)
Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region: Dzungarian Gate, Khorgos, Torugart, Khunjerab
Tibet Autonomous Region: Zhangmu, Jilong, Pulan
Customs declaration prompt after meeting the supervision requirements above:
1. Submit declaration materials for customs clearance
Bill of lading, packing list, invoice, trade contract, certificate of origin, plant quarantine certificate, China customs clearance form for imported medicinal materials or the permission of imported medicinal materials, health certificate (requirements for enterprises have ever processed and different port customs are different), ingredient testing report, label and translation documents, declaration elements, etc.
2. Declaration of intended use
For the Chinese medicinal materials declared as “medicinal”, they shall be quarantined and supervised by the customs according to the Provisions for the Supervision and Management of Entry and Exit Quarantine of Chinese Medicinal Materials, and the drug supervision and management department shall be responsible for the inspection.
For the Chinese medicinal materials declared as “edible”, that is, “homology of medicine and food, items that are both drugs and food,” they shall be quarantined and supervised according to the regulations of the General Administration of Customs on import and export food.
3. Conformity assessment for drug administration and quarantine
(1) The general process of the drug administration department: after the port drug supervision and administration department receives the declaration information – information verification - issue the Port Clearance for Import Drug - sampling - Provincial Drug Inspection Research Center inspect and issue the inspection report for imported medicinal materials. (Applicable to Chinese medicinal materials declared as “medicinal”)
(2) General customs process: after the port customs receives the declaration information - documents review - on-site inspection - laboratory quarantine - conformity assessment/unqualified disposal - taxation - issue Inspection and Quarantine Certificate for Entry Goods to release, etc.The General Administration of Chinese Customs shall assess and review the equivalence risk of the supervision system of traditional Chinese medicinal materials in the country of origin (region):
-
01
Sort out the relevant laws and regulations on animal and plant epidemics, veterinary health, public health, plant protection, enterprise registration management, etc. in the country or region where you are located, as well as written documents on the establishment and personnel of the competent authorities in the country or region and the implementation of laws and regulations. material;
-
02
Make an application. The country (region) to be exported shall submit an application for export to China to the General Administration of Chinese Customs(GACC) in writing. The General Administration of Chinese Customs initiates the access procedure and provides the proposed exporting country with a risk assessment questionnaire;
-
03
Organizational evaluation. The intended exporting country will reply according to the questionnaire, provide relevant technical information, the General Administration of Chinese Customs(GACC) will conduct risk assessment, and send an expert group to conduct overseas field inspections as needed;
-
04
The General Administration of Chinese Customs (GACC) negotiates with the competent authorities of the exporting country or region to determine the quarantine requirements for exporting Chinese medicinal materials to China based on the risk analysis, assessment and review results, negotiate and sign the relevant protocols, and determine the quarantine certificate;
-
05
The overseas enterprise shall register with the General Administration of Chinese Customs (GACC) in accordance with the specific requirements of the protocol, and the General Administration of Customs (GACC) will issue a list of products exported to China from countries or regions that meet the assessment and review requirements;
Our assistance includes but is not limited to:
* Assist in the official arrangement, translation of laws and regulations and consultation
* Assist in providing the mandatory requirements of China's national technical specifications, and carry out translation publicity.
* Assist overseas competent authorities in filing applications and consultations with China
* Assisting with some embassy consultations or providing advisory support
* Assist the commercial counselor to communicate and consult with domestic and foreign competent authorities and enterprises
* Assist in consultation with the General Administration of Chinese Customs (GACC) on laws and regulations
* Assisting overseas producers to comply with protocol access requirements and providing advisory support
(Our assistance and consultation are unofficial acts, and only provide regulatory collection, translation, sorting, opinions or adjustment strategies, and do not represent official expressions.)

The customs codes for imported Chinese medicinal materials are as follows:
GACC customs code for imported Chinese medicinal materials (Download)1. How to access botanical Chinese herbal medicines in the catalog?
Answer: If the access status of plant-derived Chinese medicinal materials is "normal", the overseas enterprises in the country do not need access application; those whose access status is "allowed to import from registered enterprises" need access registration (such as access in the past two years Greece and Afghanistan exported safflower to China). If the country and access status are not listed, the General Administration of Chinese Customs (GACC) will conduct product risk analysis and regulatory system assessment for the country or region that exports Chinese medicinal materials to China for the first time, whether the overseas manufacturers need to be registered is decided by the specific requirements of the protocol.
2. How to access Chinese herbal medicines of animal origin in the catalog?
For animal-originated Chinese herbal medicines, if the access status is "allowed to import, and registration is gradually completed", the overseas enterprises in the country do not need access application procedure; if the access status is "allowed to import from registered enterprises", access application is required. If the country is not listed, the General Administration of Chinese Customs (GACC) will conduct product risk analysis and assessment of the supervision system for the country or region that exports Chinese medicinal materials to China for the first time, whether the overseas manufacturers need to be registered is decided by the specific requirements of the protocol.
3. Do animal-derived Chinese herbal medicine need to apply for an entry animal and plant quarantine license from the customs?
Answer: Yes
4. What are the plant-derived Chinese herbal medicine that do not need to apply for an entry animal and plant quarantine license?
Answer: According to the General Administration of Customs Announcement No. 77 of 2024 (Announcement on the Cancellation of Entry Quarantine Approval for Some Animal and Plant Products), the plant-derived Chinese herbal medicine in the following:
| HS Codes | Product Name | CIQ Codes |
| 1211903999 | Other fresh, cold, frozen or dried plants (including certain parts of them, whether cut, crushed or ground into powder) mainly used as medicinal materials (Medicinal Smilax) | 1211903999142 |
| 1211903999 | Other fresh, cold, frozen or dried plants (including certain parts of them, whether cut, crushed or ground into powder) mainly used as medicines (SPATHOLOBCAULIS) | 1211903999315 |
5. Do all Chinese medicinal materials imported for "medicinal use" need to be approved for import of medicinal materials?
Answer: No, if the country of origin and product access conditions are met, if the Chinese medicinal material is listed in the "Catalogue of Non-First-Time Imported Medicinal Materials", it does not need to be processed.
6. What are the application channels and conditions for the approval of imported medicinal materials?
Answer: When importing medicinal materials for the first time, the applicant should fill in the application form for importing medicinal materials through the information system of the State Drug Administration, and submit the following materials to the local provincial drug administration:
(1) Application form for imported medicinal materials;
(2) A photocopy of the applicant's drug production license or drug business license. If the applicant is the holder of the marketing license for proprietary Chinese medicines, a photocopy of the relevant drug approval documents shall be provided;
(3) A copy of the main body registration certificate of the exporter;
(4) A copy of the purchase contract and its notarized documents;
(5) Information on the ecological environment, resource reserves, wild or planting and breeding conditions, harvesting and primary processing in the origin of medicinal materials;
(6) Standards and sources of medicinal materials;
(7) The original identification certificate of medicinal material origin issued by an institution with the qualification for identification of animal and plant origins in China, which contains the identification basis, identification conclusion, sample pictures, appraiser, identification agency and its official seal and other information.
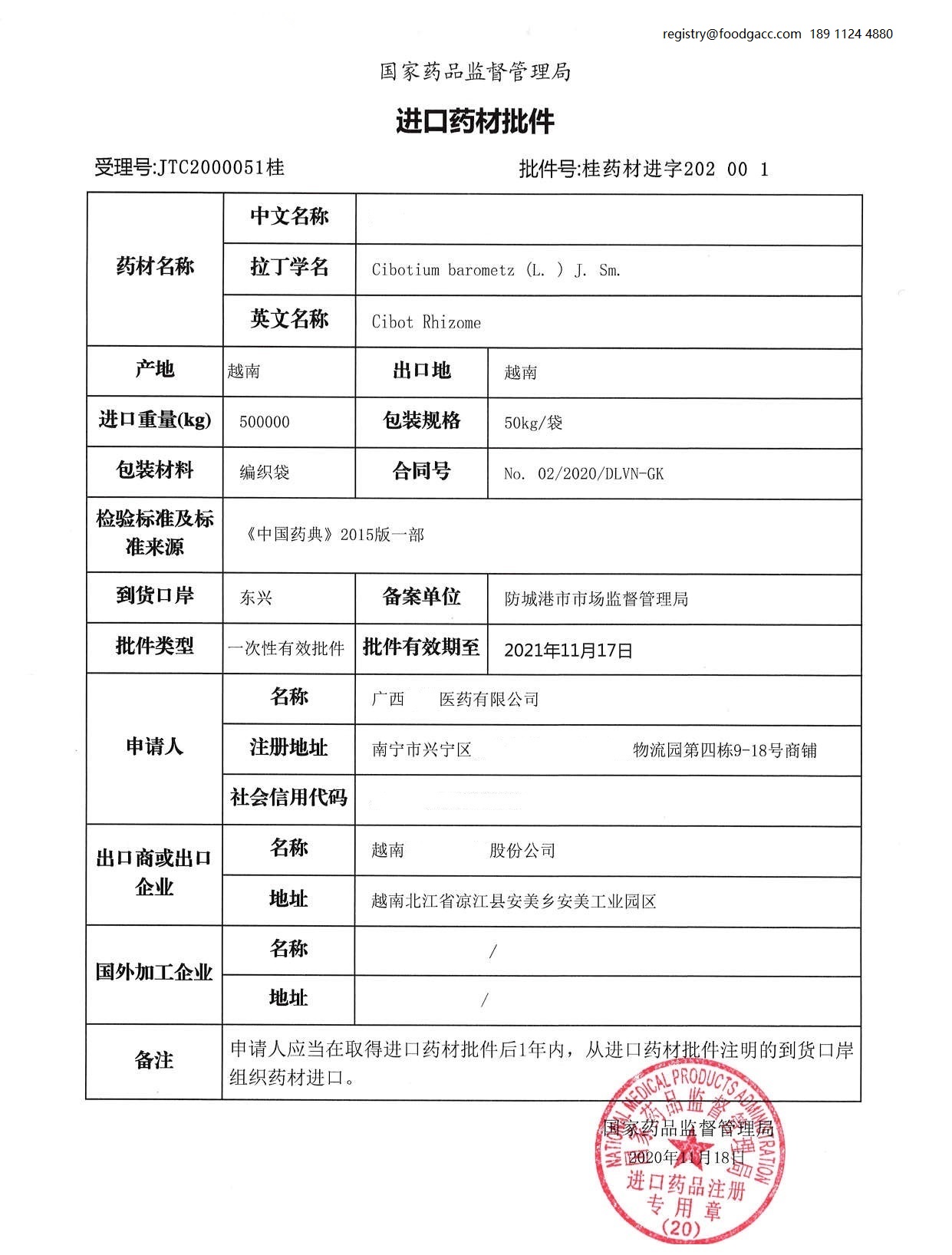
7. What is the sample of permission of imported medicinal materials?
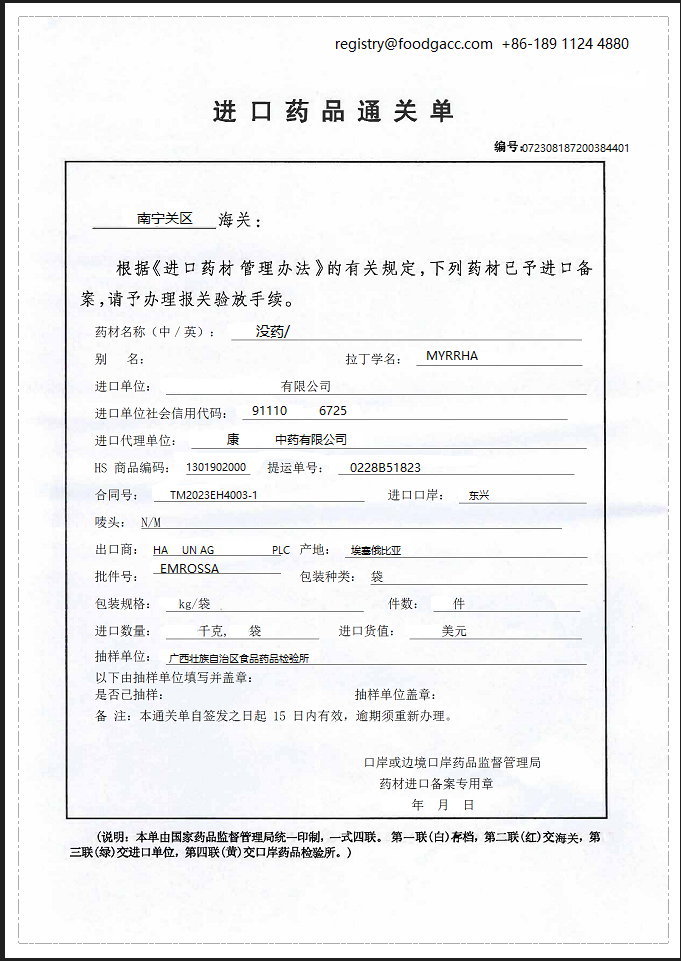
8. What is the sample of customs clearance form for non-first imported medicinal materials?
9. What are the specific contents of the catalogue of non-first-time imported medicinal materials?
|
Number |
Name |
Origin base |
Origin Place of production |
|
1 |
catechu |
Peeled branch, dried dry decoction of legume catechu Acacia catechu (L. f.) Willd. |
Indonesia, Malaysia, Myanmar |
|
2 |
American Ginseng |
Dried roots of Panax quinquefolium L. of the Araliaceae plant |
Canada, USA |
|
3 |
Korean red ginseng
|
Steamed dry roots of the 6-year-old cultivar Panax ginseng C. A. Mey |
South Korea |
|
4 |
saffron |
Dried stigma of Crocus sativus L., Iridaceae |
Iran, Spain, Italy, Germany, France, Greece, India, Japan, Afghanistan |
|
5 |
Sioux |
The balsam resin exuded from the trunk of the witch hazel tree Liquidambar orientalis Mill. is processed and refined |
UK, Turkey, Egypt, Indonesia |
|
6 |
Frankincense |
Resin exuded from the bark of Boswellia carterii Birdw. and Boswellia bhaw-dajiana Birdw. of the olive family Boswellia |
Ethiopia, Kenya, Somalia, Sudan |
|
7 |
myrrh |
Dried resin of the olive plant Commiphora myrrha Engl. or Hadidin Commiphora molmol Engl. |
Somalia, Kenya, Ethiopia |
|
8 |
dried blood |
Processed resin exuded from the fruit of the palm plant Daemonorops draco Bl. |
Singapore, Indonesia, Malaysia |
|
9 |
Agarwood |
Rhizoma Aquilaria Aquilarla agallocha Roxb. Wood containing resin |
Indonesia, Malaysia, Vietnam |
|
10 |
sandalwood |
Dried heartwood of the trunk of Santalum album L. |
India, Indonesia, Timor-Leste, Australia |
|
11 |
cloves |
Dried flower buds of Eugenia caryophyllata Thunb. |
Zanzibar, Sri Lanka, Indonesia, Madagascar, Brazil |
|
12 |
cumin |
Dried ripe fruit of the Umbelliferae plant Foeniculum vulgare Mill. |
Indonesia, India, Iran, Turkey |
|
13 |
longum |
Dried near-ripe or ripe ear of Piper longum L. |
Indonesia, Philippines, Vietnam |
|
14 |
Cardamom |
Dried ripe fruit of Amomum kravanh Pierre ex Gagnep. or Amomum compactum Soland ex Maton of Zingiberaceae |
Indonesia, Thailand, Cambodia |
|
15 |
Nutmeg |
Dried kernels of Myristica fragrans Houtt. of Myristica fragrans Houtt. |
Indonesia, Sri Lanka, Malaysia, India, Nepal |
|
16 |
big belly |
Dried peel of the palm plant Areca catechu L. |
Indonesia, Myanmar, India, Malaysia, Vietnam, Pakistan, Thailand, Philippines, Cambodia |
|
17 |
big wind |
Dried ripe seeds of Hydnocarpus anthelmintica Pierre |
Thailand, Vietnam, Malaysia |
|
18 |
Western Green Fruit |
Dried young fruit of the Clivia plant Terminalia chebula Retz. |
India, Myanmar, Malaysia |
|
19 |
myrobalan |
The dried ripe fruit of Terminalia chebula Retz. or Terminalia chebula Retz. var. tomentella Kurt. |
India, Indonesia, Myanmar, Sri Lanka, Nepal |
|
20 |
fat sea |
Dried ripe seeds of Sterculia lychnophora Hance |
Thailand, Vietnam |
|
21 |
aloe vera |
Aloe barbadensis Miller of Liliaceae, Aloe ferox Miller of Cape of Good Hope, or the dried sap of leaves of other related plants in the same genus |
Curacao, Aruba, Bonaire, Kenya |
|
22 |
monkey jujube |
From the abomasum (the fourth stomach of a ruminant) of the goat Capra hircus, formed after the goat has eaten acacia seeds, small pieces of wood, pebbles, or other foreign objects |
India |
|
23 |
Cinnamon |
Dried bark of Lauraceae plant Cinnamomum loureiri Nees |
Myanmar, Vietnam |
|
24 |
Senna |
Dried leaflets of the legume Cassia angustifolia Vahl or Cassia acutifolia Delile |
India, Egypt, Myanmar |
|
25 |
horse money |
Dry ripe seeds of Strychnos nux-vomica L. of the Strychnaceae plant |
India, Thailand, Myanmar |
|
26 |
Tianzhu yellow |
Dried lumps of exudates from the culms of Poaceae Bambusa textilis McClure or Schizostachyum chinese Rendle |
Indonesia, Singapore, Thailand, Malaysia |
|
27 |
hippocampus |
Dried body of Hippocampus kelloggi Jordan et Snyder, Hippocampus histrix Kaup, Hippocampus kuda Bleeker, Hippocampus trimaculatus Leach or Hippocampus ja ponicus Kaup |
Thailand, Malaysia, Philippines, Singapore, Indonesia |
|
28 |
Gecko |
Dried body of the gecko gecko Gekko gecko Linnaeus |
Thailand, Indonesia, Cambodia |
|
29 |
Korean Red Ginseng |
Steamed dried roots of Panax ginseng C. A. Mey, a 6-year-old cultivar of Araliaceae |
North Korea |
|
30 |
Dendrobium |
Fresh or dried stems of orchids Dendrobium nobile Lindl., Dendrobium chrysotoxum Lindl. or Dendrobium fimbriatum Hook |
Thailand, Laos, Vietnam, Myanmar |
|
31 |
Amomum |
Dried ripe seeds and fruits of Amomum xanthioides Wall |
Japan, Myanmar, Vietnam, Thailand, Indonesia |
|
32 |
Tsaoko |
Dried ripe fruit of Amomum tsao-ko Crevost et Lemaire |
India |
|
33 |
gallic |
Dried galls on young branches of beech tree Quercus infectoria Oliv |
Turkey, Iran, Greece, India |
|
34 |
wooden butterfly |
Dried mature seeds of Oroxylum indicum (L.) Vent. |
Myanmar |
|
35 |
Fang catecha |
Rubiaceae Uncaria catechu Uncaria gambier (Hunter) Roxb. Dry decoction with leafy twigs |
Malaysia, Indonesia, Myanmar |
|
36 |
Antelope horn |
Horns of the bovine saiga Saiga tatarica Linnaeus |
Russia |
|
37 |
Benzoin |
Dried resin of Styrax tonkinensis (Pierre) Craib ex Hart. |
Thailand, Vietnam, Laos |
|
38 |
Garcinia Cambogia |
Garcinia garcinia hanbyryi Hook f. resin oozing from the trunk |
Thailand, India |
|
39 |
female cloves |
Dried near-ripe fruit of Eugenia caryophyllata Thunb. of the Myrtaceae plant |
Zanzibar, Madagascar, Sri Lanka |
|
40 |
Fairy Guangtian |
Dried seeds of Hygrophila megalantha Merr. |
Vietnam, Myanmar |
|
41 |
betel nut |
Dried ripe seeds of the palm plant Areca catechu L. |
Indonesia, Myanmar, India, Malaysia, Vietnam, Pakistan, Thailand, Philippines, Cambodia |
|
42 |
Hu Huanglian |
Dried rhizome of Picrorhiza scrophulariiflora Pennell |
India, Nepal |
|
43 |
Tortoiseshell |
Carapace (spine scales and rib scales) of the turtle Eretmochelys imbricata (Linnaeus) |
Indonesia, Philippines |
|
44 |
Cassia Shi |
Shells of Haliotis diversicolor Reeve, Haliotis discus hannai Ino, Haliotis ovina Gmelin, Haliotis ruber (Leach), Haliotis asinina Linnaeus or Haliotis laevigata (Donovan) |
Japan, Australia, New Zealand, Indonesia |
|
45 |
seal kidney |
Sea lion seals Callorhinus ursinus Linnaeus. dry male external genitalia (penis and testes) |
America / Canada |
|
46 |
sea dragon |
Syngnathus Diaohailong Solenognathus hardwickii (Gray), multi-thorn Diaohailong Syngnathus guntheri Dunker's dry body |
Thailand, Indonesia |
|
47 |
Asafetida |
Oleoresin collected from fresh rhizomes and roots of Ferula assafoetida L. and other plants of the same genus |
Iran, Afghanistan, India |
|
48 |
deer whip |
Dried penis and testicles of cervus sika deer Cervus nippon Temminck or red deer Cervus elaphus Linnaeus |
New Zealand, Australia |
|
49 |
deer tail |
Dried tail of red deer Cervus elaphus Linnaeus or sika deer Cervus nippon Temminck |
New Zealand, Australia |
|
50 |
Natural Borneol (D-borneol) |
The fresh branches and leaves of Lauraceae Cinnamomum camphora (L.) Presl are extracted and processed |
Indonesia |
|
51 |
Sophora japonica |
Dried flowers and buds of the legume Sophora japonica L. |
Vietnam |
|
52 |
Licorice |
Dried roots and rhizomes of the legume Glycyrrhiza uralensis Fisch., Glycyrrhiza inflata Bat. or Glycyrrhiza glabra L. |
Pakistan, Afghanistan, Tajikistan, Uzbekistan, Kazakhstan, Azerbaijan, Kyrgyzstan, Turkmenistan |
|
53 |
Ibemus |
Dry bulb of Fritillaria walujewii Regel or Fritillaria pallidiflora Schrenk of Liliaceae |
Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan |
|
54 |
Pangosaurus |
Dried rhizomes of Dioscorea nipponica Makino, Dioscorea nipponica |
North Korea |
|
55 |
Cistanche |
Dried fleshy stems with scaly leaves of Cistanche deserticola Y.C.Ma or Cistanche tubulosa (Schenk) Wight |
Turkmenistan, Kazakhstan |
|
56 |
Guan Huangbai |
Dried bark of Phellodendron amurense Rupr. |
North Korea |
|
57 |
Schisandra |
Dried ripe fruit of the Magnoliaceae Schisandra chinensis (Turcz.) Baill. |
North Korea |
|
58 |
Asarum |
Dried roots and rhizomes of Asarum heterotropoides Fr. Schmidt var. mandshuricum (Maxim.) Kitag., Asarum sieboldii Miq. var. seoulense Nakai or Asarum sieboldii Miq. |
North Korea |
|
59 |
Windproof |
Dried root of Umbelliferae windbreak Sposhnikovia divaricata (Turcz.) Schischk. |
Mongolia, Russia |
|
60 |
Turmeric |
Dried rhizomes of the ginger plant Curcuma longa L. |
Indonesia, Myanmar, India |
|
61 |
Cassia |
Dried mature seeds of the legume Cassia obtusifolia L. or Cassia tora L. |
India, Nepal |
|
62 |
Mao myrobalan |
The dried ripe fruit of the Gentianaceae plant Terminalia bellirica (Gaertn.) Roxb. |
India, Nepal |
|
63 |
Empress |
Dried ripe fruit of Phyllanthus emblica L., Euphorbiaceae |
India, Nepal |
|
64 |
Jujube |
Dried ripe fruit of the Anacardiaceae plant Choerospondias axillaris (Roxb.) Burtt et Hill |
India, Nepal |
|
65 |
Tibetan madder |
Rubia family Rubia wallichiana Decne. and Tibetan Rubia R.tibetica Hook.f. and dried roots and rhizomes of several plants of the same genus |
India, Nepal |
|
66 |
Indian Sweater |
Gentianaceae Swertia chirayita (Roxb. ex Flemi) Karsten dry whole herb |
India, Nepal |
|
67 |
Comfrey |
The female body of Laccifer lacca Kerr., a lacquer, parasitizes the trunks of various plants, such as Dalbergia L. f. and Eriolaenea DC. thing |
India, Nepal |
|
68 |
Broad vine |
Dried stems of Tinospora cordifolia (wulld) Miers or T. sinensis (Lour.) Merr. |
India, Nepal |
|
69 |
big stipule |
Dried mature seeds of legume Caesalpinia crista L. |
India, Nepal |
|
70 |
white fresh skin |
Dried root bark of Dictamnus dasycarpus Turcz. |
North Korea, Russia |
|
71 |
northern bean root |
Dried rhizome of Menispermum dauricum DC. |
North Korea |
|
72 |
Psoralea |
Dried ripe fruit of the legume Psoralea corylifolia L. |
India, Myanmar |
|
73 |
Poria |
Dried sclerotia of Poria cocos (Schw.) Wolf |
Madagascar |
|
74 |
Drynariae |
Dried rhizomes of Quercus Drynaria fortunei (Kunze) J. Sm. |
Myanmar |
|
75 |
black seed |
Dried mature seeds of Ranunculaceae Nigella glandulifera Freyn et Sint. |
Pakistan |
|
76 |
Safflower |
Dried flowers of safflower Carthamus tinctorius L. |
Kazakhstan |
|
77 |
Mistletoe |
Dry leafy stem branch of Viscum coloratum (Komar.) Nakai |
Ukraine |
|
78 |
Polygonatum |
Dried rhizomes of Liliaceae Polygonatum kingianum Coll.et Hemsl., Polygonatum sibiricum Red. or Polygonatum cyrtonema Hua |
Nepal |
|
79 |
Scutellaria |
Dry root of Scutellaria baicalensis Georgi |
Russia |
|
80 |
Chickweed |
Dried whole plant of the legume Abus cantoniensis Hance |
Myanmar |
|
81 |
mustard seeds |
Dried mature seeds of the cruciferous plant Sinapis alba L. or Brassica juncea (L. ) Czern. et Coss. |
Mongolia |
|
82 |
Honeysuckle |
Dried flower buds or with first blooms of the honeysuckle Lonicera japonica Thunb. |
North Korea |
|
83 |
Bitter almonds |
Dry ripe seeds of Rosaceae Prunus armeniaca L. var. ansu Maxim., Siberian apricot Prunus sibirica L., Northeastern apricot Prunus mandshurica (Maxim.) Koehne or apricot Prunus armeniaca L. |
North Korea |
|
84 |
Lingzhi |
Dried fruiting body of Polyporaceae fungus Ganoderma lucidum (Leyss. ex Fr. ) Karst. or Ganoderma sinense Zhao, Xu et Zhang |
America |
|
85 |
Vitex |
Dried ripe fruit of the Verbena plant Vitex trifolia L. var. simplicifolia Cham. or Vitex trifolia L. |
Myanmar |
|
86 |
Equisetum |
Dry aerial part of the Equisetum Equisetum hyemale L. |
North Korea |
|
87 |
Nansha ginseng |
Dried root of Adenophora tetraphylla (Thunb. ) Fisch or Adenophora stricta Miq. |
North Korea |
|
88 |
Gentiana |
Dry roots of Gentiana Gentiana macrophylla Pall., Gentiana straminea Maxim., Gentiana crassicaulis Duthie ex Burk. or Gentiana dahurica Fisch. |
Russia |
|
89 |
Cimicifuga |
Dried rhizomes of Ranunculaceae Cimicifuga heracleifolia Kom., Cimicifuga dahurica (Turcz.) Maxim. or Cimicifuga foetida L. |
North Korea |
|
90 |
pine pollen |
Dried pollen of Pinus massoniana Lamb., Pinus tabulieformis Carr. or several species of the same genus |
North Korea |
|
91 |
Wei Lingxian |
Dried roots and rhizomes of Ranunculaceae Clematis chinensis Osbeck, Clematis hexapetala Pall. or Northeast Clematis manshurica Rupr. |
North Korea |
|
92 |
Curcuma |
Dried rhizomes of Curculigo orchioides Gaertn. |
Myanmar |
|
93 |
Polygonatum |
Dried rhizomes of Polygonatum ordoratum (Mill.) Druce of Liliaceae |
North Korea |